Cloning private repositories on GitHub requires authentication. Since GitHub removed password-based authentication, the recommended way is to use a Personal Access Token (PAT). In this guide, I’ll walk you through how to securely clone your private GitHub repository using a Personal Access Token — step by step.
🔒 What Is a Personal Access Token?
A Personal Access Token (PAT) is a secure alternative to your GitHub password. It allows you to authenticate Git operations (like clone, pull, or push) over HTTPS. Tokens can be fine-tuned with specific permissions and expiration dates, making them safer than traditional passwords.
💡 Think of a PAT as a temporary key that grants your system limited access to your GitHub repositories.
🧭 Step 1: Generate a Personal Access Token
1. Log in to GitHub
Go to github.com and sign in to your account.
2. Open Developer Settings
Click on your profile picture → Settings → scroll down → Developer settings.

3. Create a New Token
Navigate to:
Personal access tokens → Tokens (classic) or Fine-grained tokens
Click Generate new token.

4. Configure the Token
- Note: Give your token a descriptive name (e.g., “Private Repo Clone”).
- Expiration: Choose a suitable expiration period (e.g., 30 or 90 days).
-
Scopes/Permissions:
For cloning a private repo, enable:-
repo→ Full control of private repositories - Optionally,
read:orgif the repo is under an organization.
-

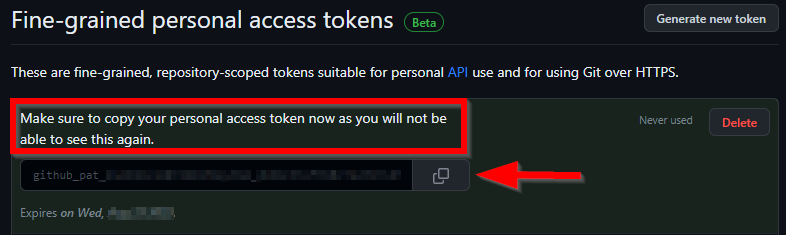
5. Generate and Copy
Click Generate token and copy it immediately — GitHub won’t show it again!
💻 Step 2: Clone the Private Repository
A. Copy Your Repository URL
In GitHub, go to your private repository → click Code → copy the HTTPS URL.
Example:
https://github.com/manojdamor/private-project.git

B. Clone Using the Token
Now open your terminal (or Git Bash) and run:
git clone https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
When prompted for a username, enter your GitHub username.
When asked for a password, paste the Personal Access Token you generated.
Example:
git clone https://github.com/manojdamor/private-project.git
Username: manojdamor
Password: <paste your token here>
✅ Git will now clone your private repository locally.
Alternative: Inline Token (Quick Method)
You can also embed the token directly in the URL (not recommended for shared systems):
git clone https://<TOKEN>@github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
Example:
git clone https://ghp_abcd123XYZ456@github.com/manojdamor/private-project.git
⚠️ Warning: Avoid this method if others share your machine, since the token will be stored in your shell history.
🔁 Step 3: (Optional) Save Your Credentials
If you frequently work with GitHub, store your credentials so you don’t have to enter the token every time:
git config --global credential.helper store
Next time you clone or push, Git will remember your credentials.
🧹 Step 4: Manage and Revoke Tokens
Go back to Settings → Developer settings → Personal access tokens anytime to:
- View your active tokens
- Revoke old ones
- Generate new ones

🔐 Tip: Rotate tokens regularly and delete any that are no longer needed.
🚀 Final Thoughts
Using a Personal Access Token is now the official and most secure way to clone private repositories from GitHub. It ensures better control, transparency, and safety compared to passwords.
Whether you’re a developer, editor, or creator storing project files in private repos, PATs make your workflow smooth and secure.
Written by: Manoj Damor
Web Developer & Tech Creator
Travel with Manoj – YouTube Channel

Leave a Reply